Understanding Food Security Dynamics
The GCC procures 85% of its food requirements from overseas, making food security a key challenge in a time of worsening climate disasters. Approximately 85% of GCC countries’ food is imported. This proportion rises to 90% for cereals, and almost 100% of rice is imported. This overdependence on foreign production creates significant vulnerabilities in the GCC nations’ food supply chains. The vulnerability of these systems was conveniently demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic just a few years ago.
The Middle East remains one of the most import-dependent regions globally for essential food products such as dairy, meat, fruits, and vegetables. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, Iraq and Egypt are central to this market, which continues to grow as consumer demand for high-quality and ethically sourced products rises. Alongside this trend, the global halal market is expanding rapidly, influencing the region’s food import strategies and preferences.
As the global halal food market is expected to reach $5.8 trillion by 2032, the Middle East has cemented its role as a crucial hub for the halal food industry. This growth is driven by increased demand for halal-certified meat, dairy, and other food products, not just from Muslim consumers but also from non-Muslims who prioritize ethical consumption.
GCC Countries Regard Food Security as a Critical Issue that Concerns Many Nations & Regional & International Organisations, Affirms that the General Secretariat, Through its Strategic Partnerships, Places this Issue at the Top of its Priorities: Their Excellencies, members of the GCC Agricultural Cooperation and Food Security Committee, discussed several important topics related to joint cooperation in agriculture, livestock, fisheries and food security among the GCC countries, and made appropriate decisions regarding them.
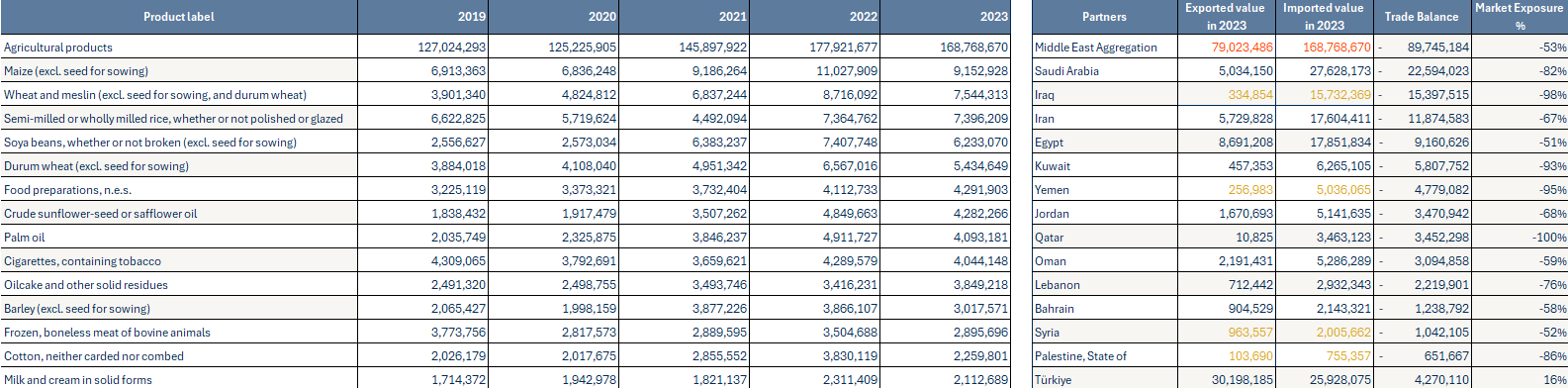
Trade Dynamics of Agricultural Products of countries in the Middle East in US$ Thousand
Explore import bill of agricultural products and trade statistics of agricultural products in the Middle Eastern market
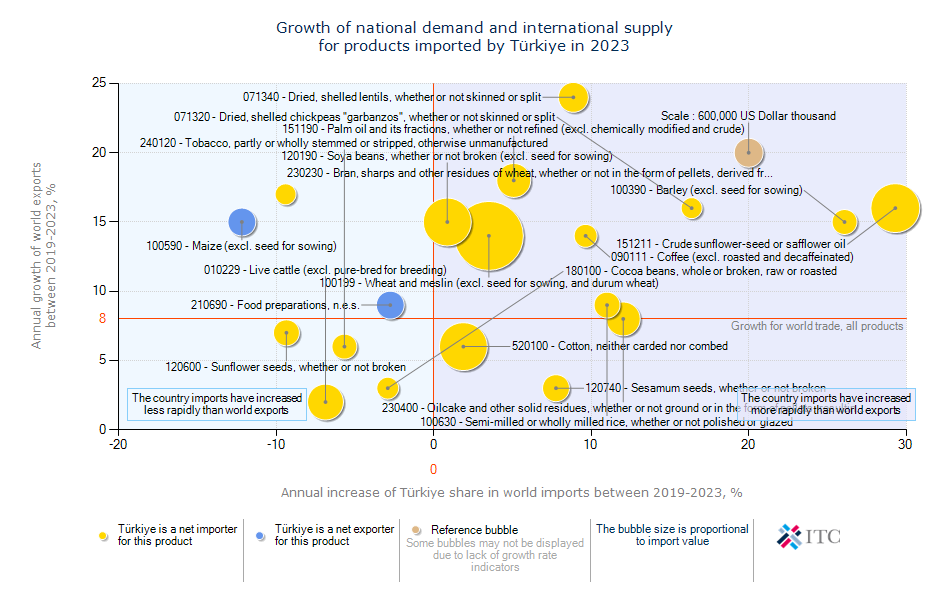
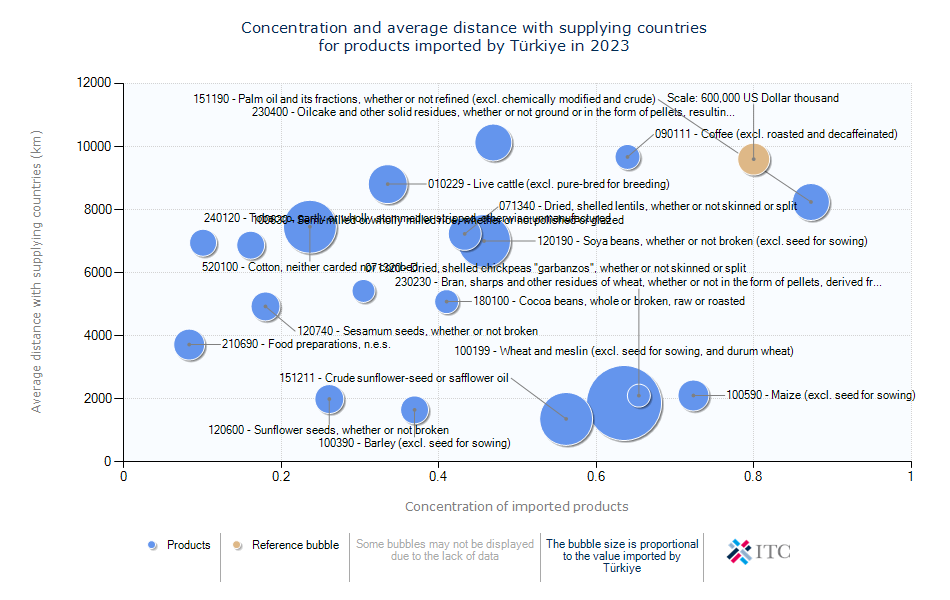
Türkiye's Agricultural Import Trends 2023
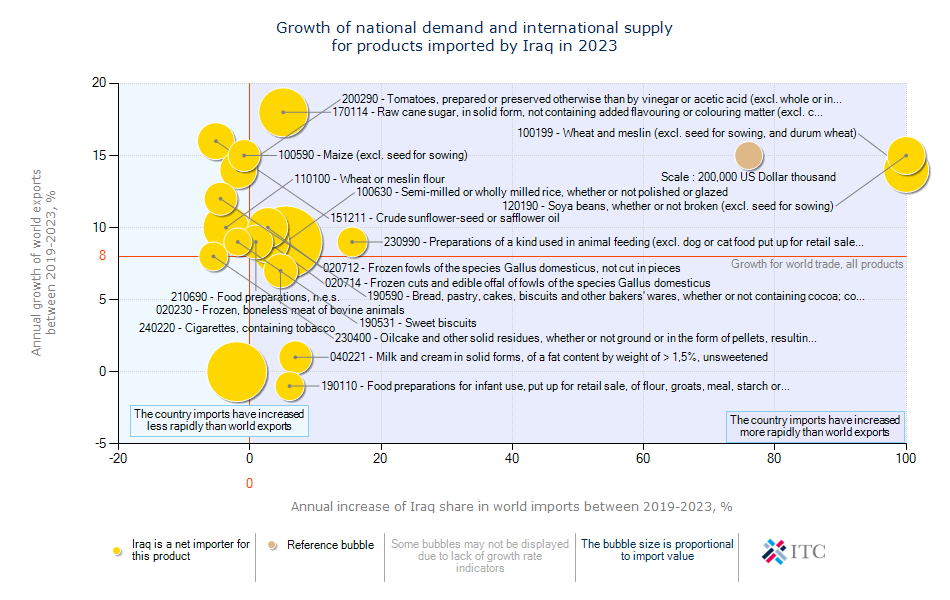
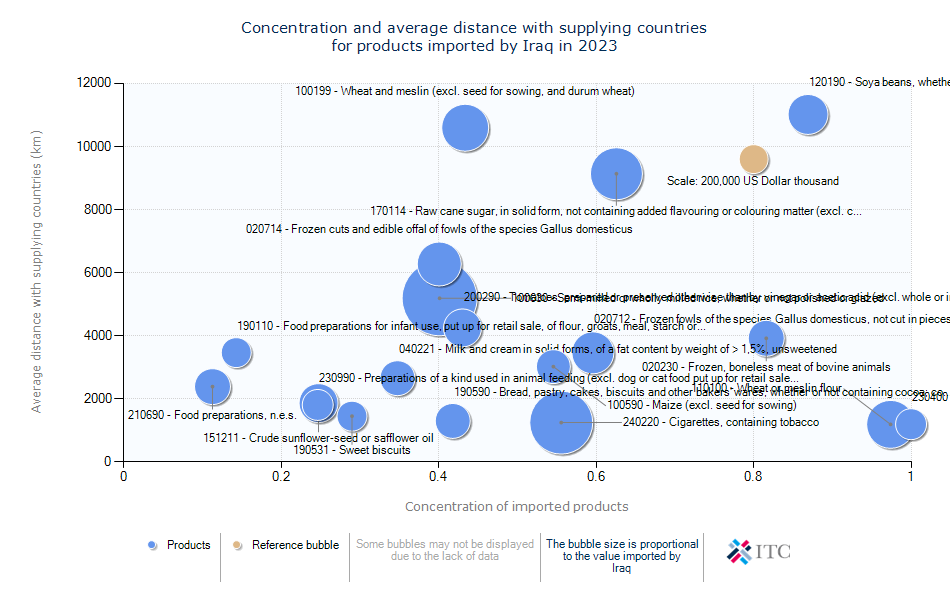
Iraq's Agricultural Import Trends 2023
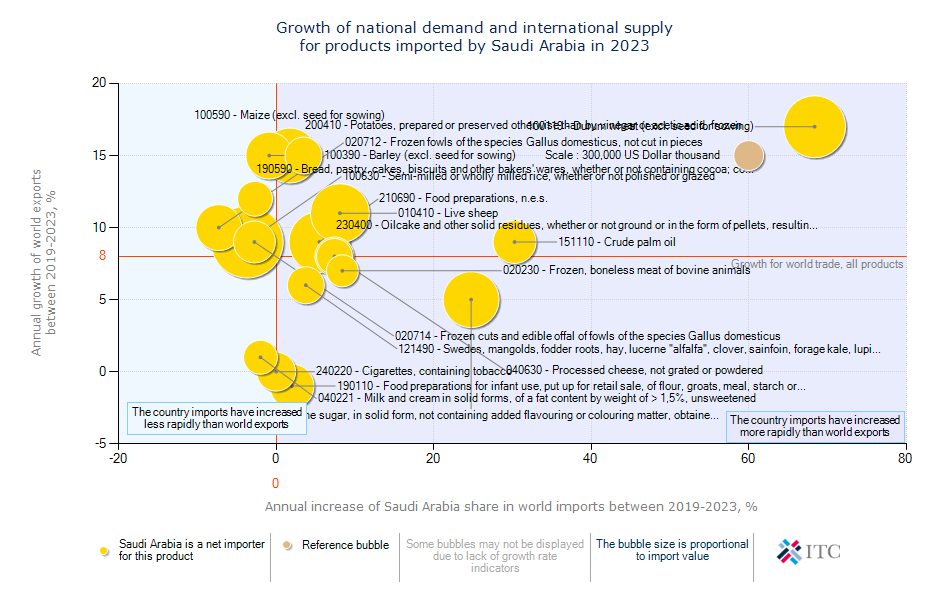
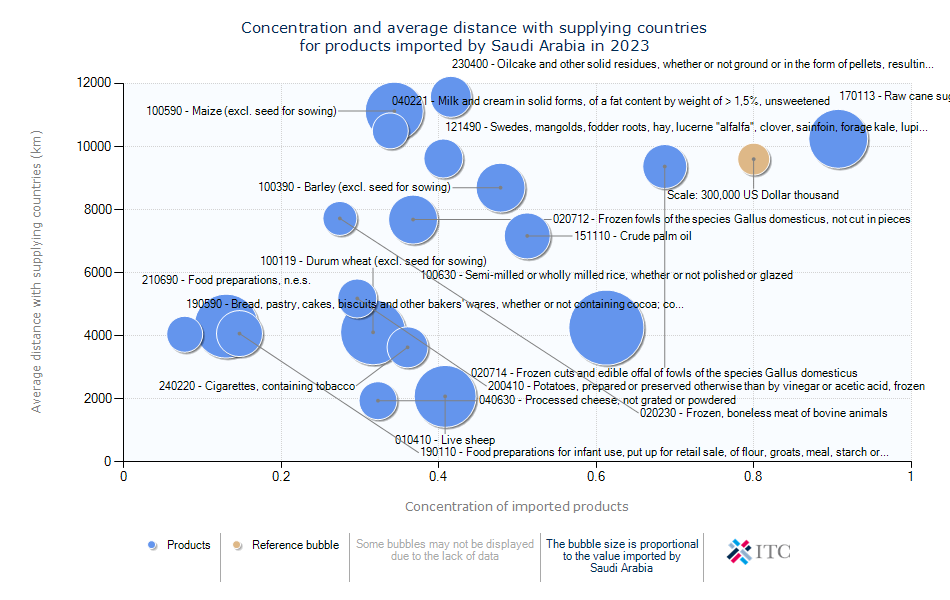
Saudi Arabia's Agricultural Import Trends 2023
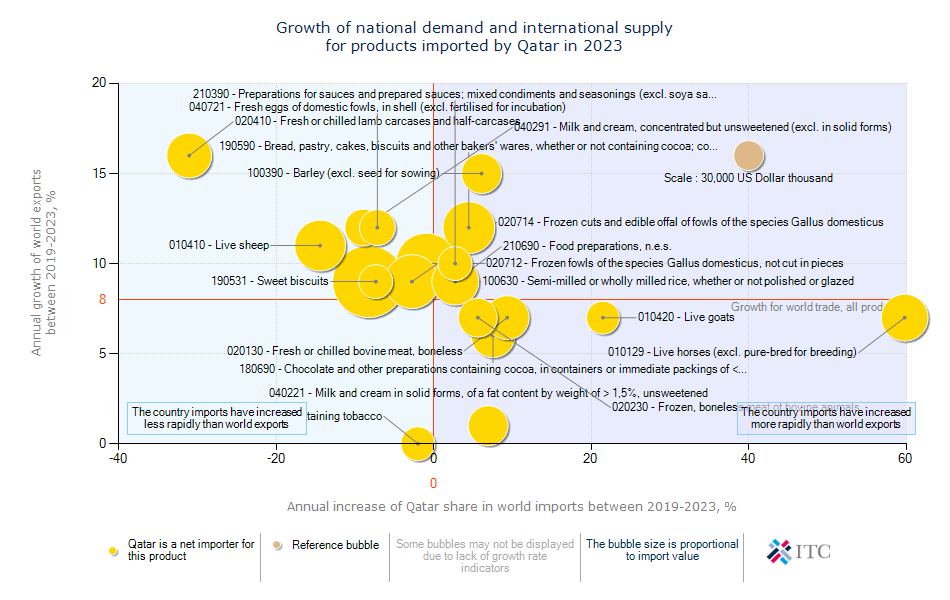
Qatar's Agricultural Import Trends 2023
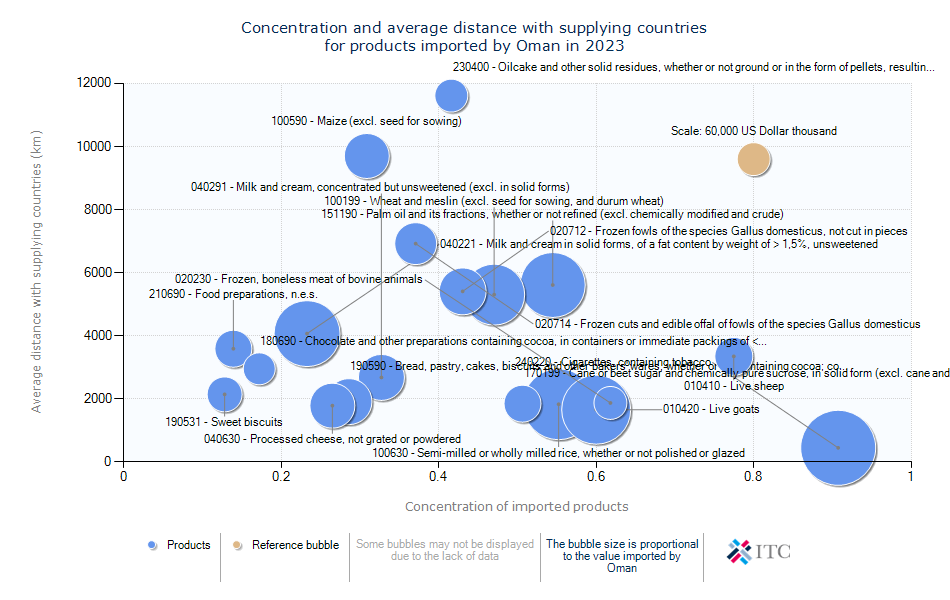
Oman's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023

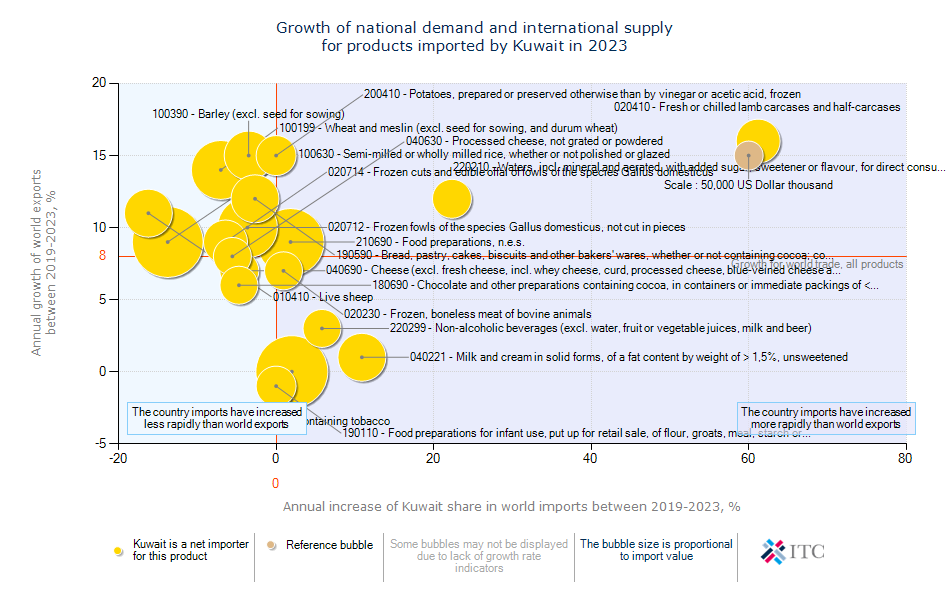
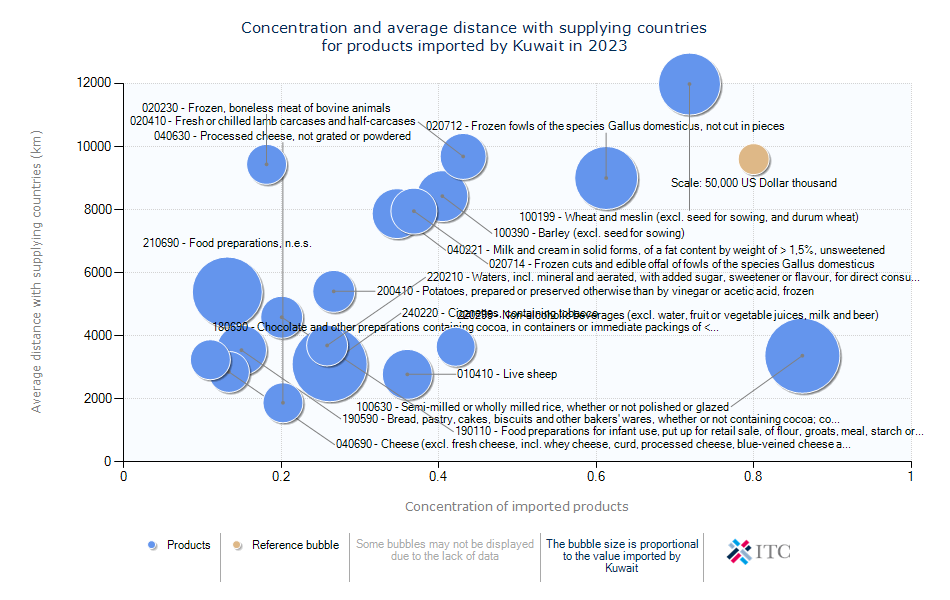
Kuwait's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023
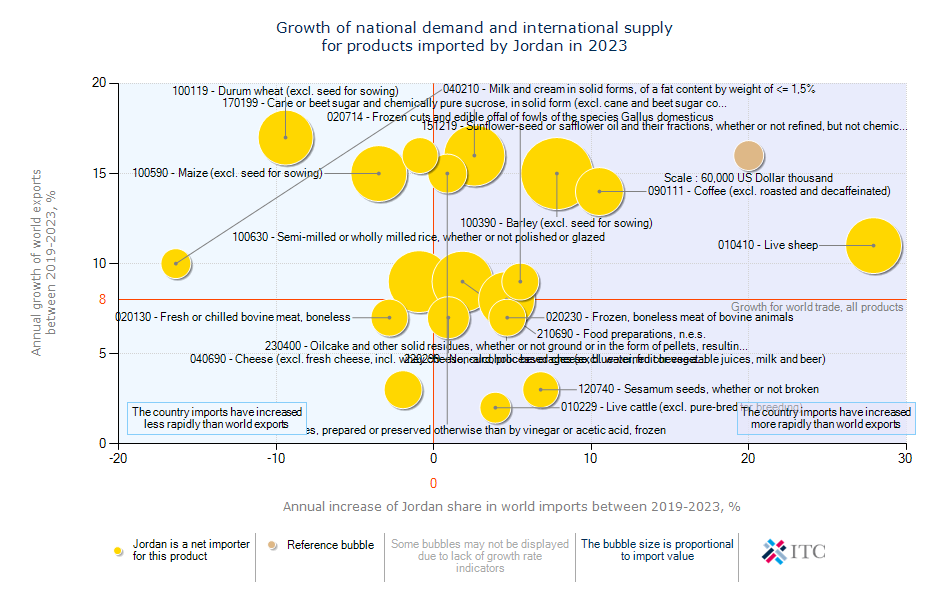
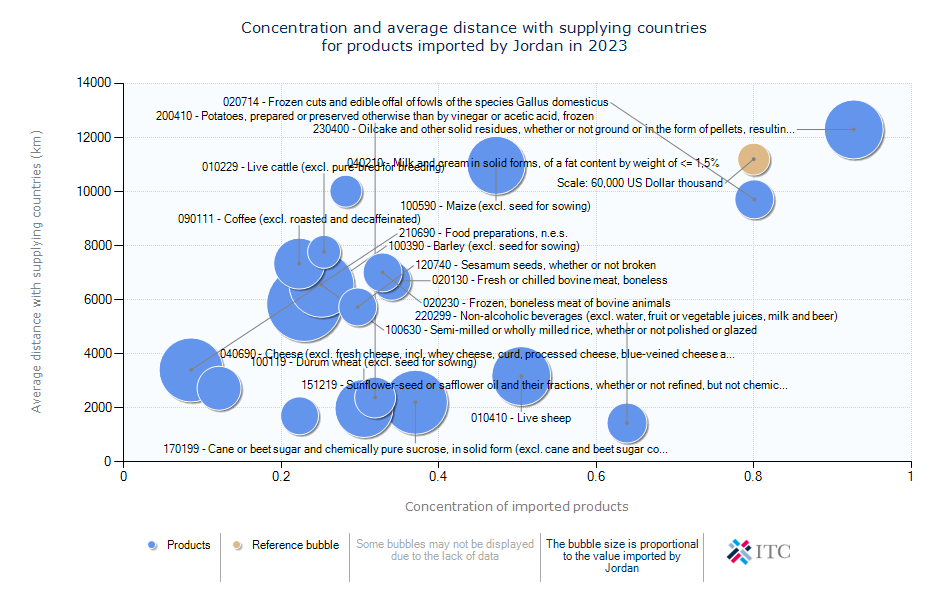
Jordan's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023
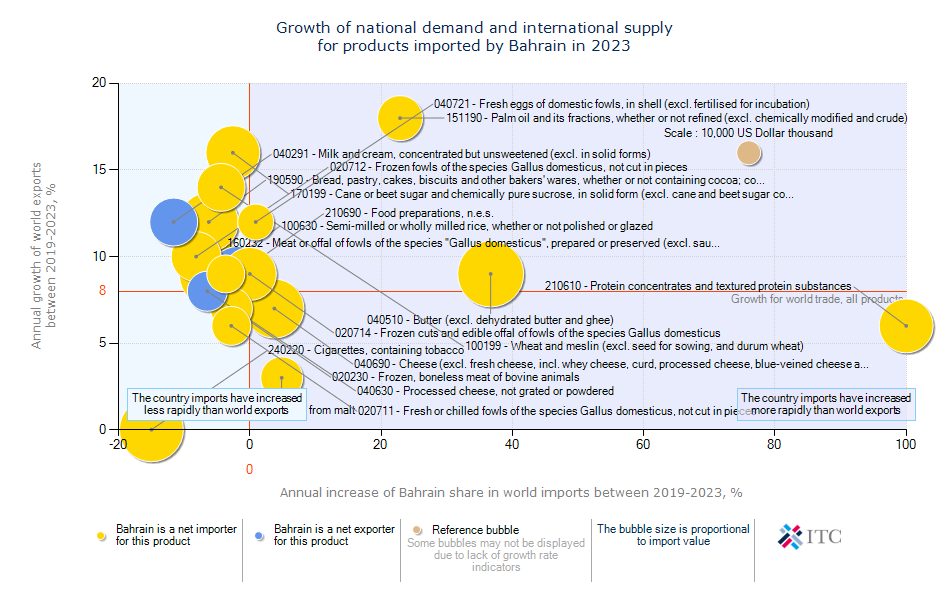
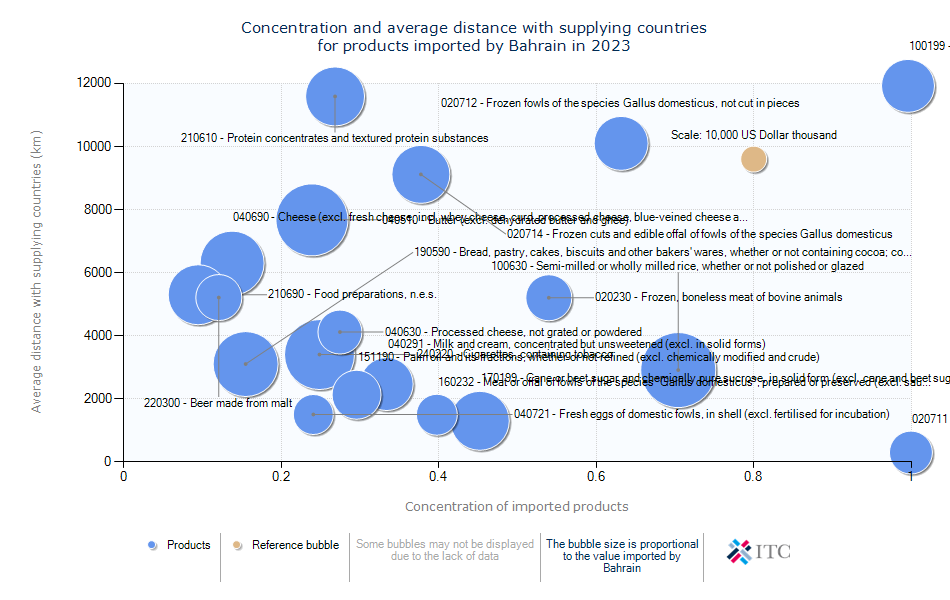
Bahrain's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023
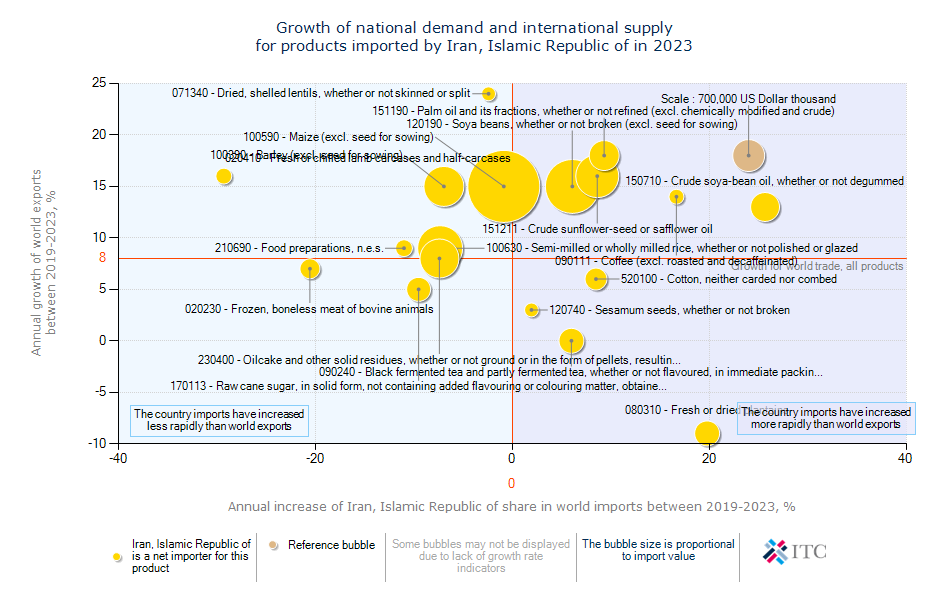
Iran's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023

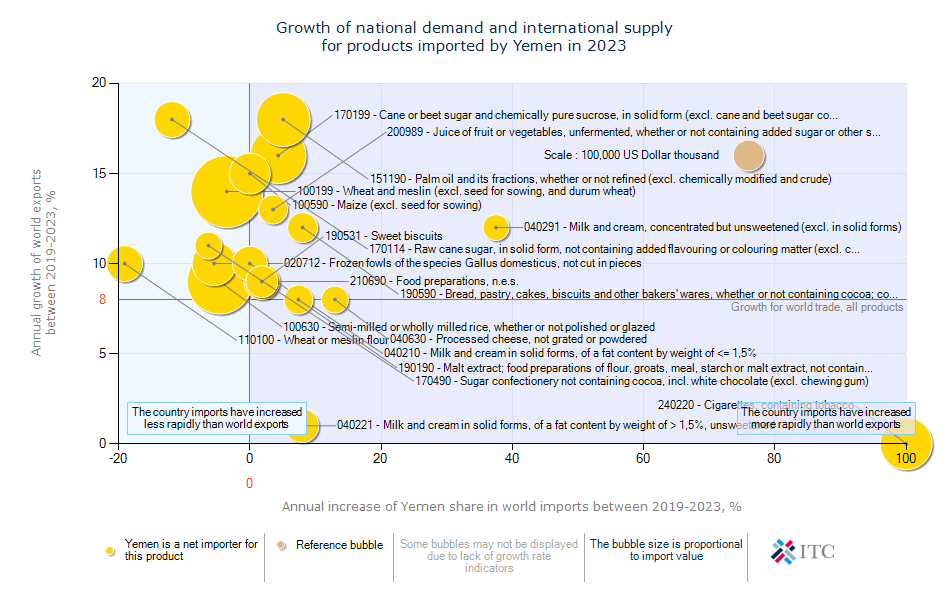
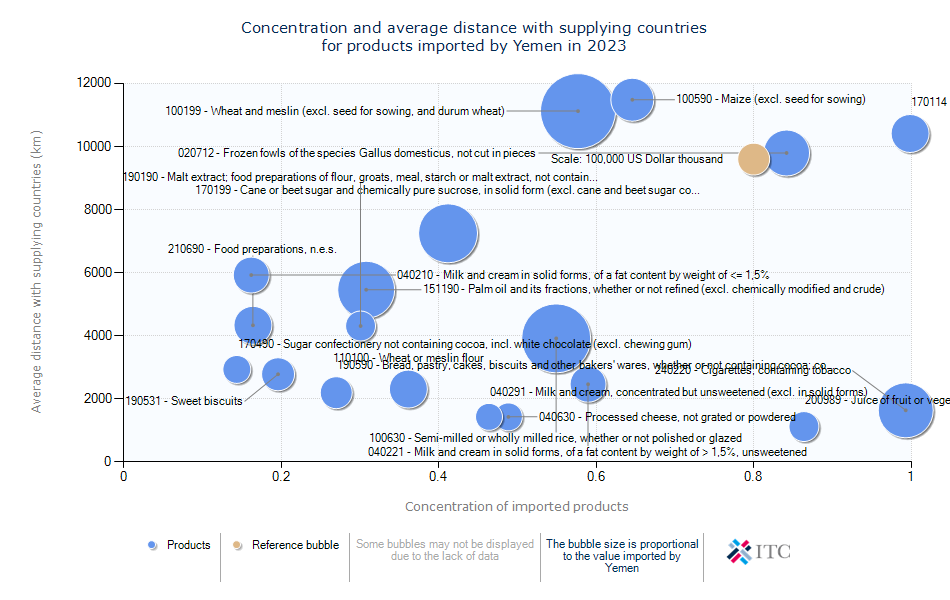
Yemen's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023
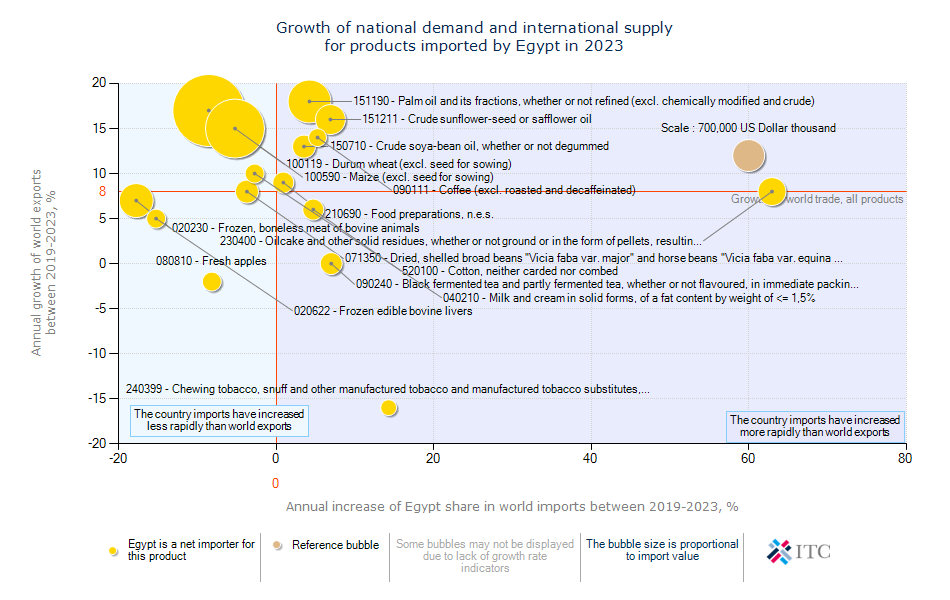
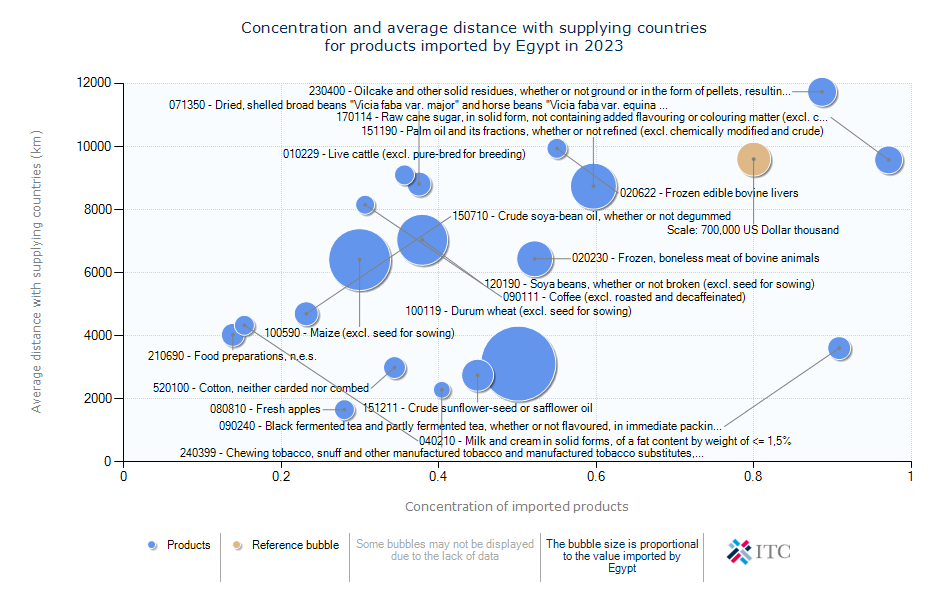
Egypt's Agricultural Import Dynamics 2023
Key Halal Product Categories
Major Players in the Halal Market
Major Exporters:
Brazil: The largest exporter of halal products, particularly meat, supplying significant quantities to the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
India: A key supplier of halal-certified meat and processed food.
Australia: A major exporter of halal beef and lamb, with a strong market presence in the Middle East.
Malaysia: Known for its high standards in halal certification, Malaysia exports a variety of halal-certified processed foods.
Major Importers:
Indonesia: The largest halal food market by value, importing a wide range of halal products.
Saudi Arabia: A significant importer of halal-certified meat and other food products.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): Acts as a regional hub for halal food imports, facilitating distribution across the Gulf.
Malaysia: Both a producer and a significant consumer of halal products, especially processed foods.





